WiFi Security: 3 Simple Steps to Secure Your Router
WiFi security should be at the top of your priority list in today’s connected world. Every day, countless home networks are targeted by hackers looking for valuable personal information or simply trying to piggyback on your internet connection. According to cybersecurity experts, the average unsecured home WiFi network can be compromised in less than 5 minutes by someone with basic hacking tools. Despite this alarming statistic, a surprising 20% of home networks still use weak security protocols or default passwords.
Think of your WiFi network as the front door to your digital home. Would you leave your front door wide open when you’re not home, with a sign saying “Come on in, take what you want”? Of course not! Yet that’s essentially what an unsecured WiFi network invites. Proper WiFi security not only protects your personal data from theft but also ensures your network runs smoothly without unauthorized users slowing down your connection.
Ready to transform your vulnerable network into a digital fortress? Let’s explore the simple yet effective ways to boost your WiFi security and keep digital intruders at bay.
Table of Contents
What is WiFi Security?
Have you ever wondered what actually happens when you click that little lock icon in your WiFi settings? WiFi security refers to the protective measures implemented to safeguard your wireless network from unauthorized access and potential threats. It’s essentially your network’s immune system, defending against digital pathogens that want to infect your online life.
Here’s a fun fact: hackers often drive around neighborhoods in a practice called “wardriving,” using specialized software to detect unsecured networks they can easily infiltrate. Your WiFi signal doesn’t stop at your walls—it can reach much farther than you might expect, sometimes extending to the street or neighboring buildings!
Don’t worry, though—you don’t need to be a tech genius to secure your network effectively. With the right knowledge and a few minutes of your time, you can significantly strengthen your WiFi security and enjoy peace of mind knowing your digital life is well-protected.
Why You Should Secure Your WiFi Network
Protect Your WiFi Security From Unauthorized Access
An unsecured WiFi network is an open invitation for neighbors, passersby, and potential hackers to connect to your internet service. This unauthorized access doesn’t just slow down your connection—it creates serious security vulnerabilities. When strangers connect to your network, they can potentially monitor your online activities, access shared files on your network, or use your internet for illegal activities that could be traced back to you.
Safeguard Personal Information With Proper WiFi Security
Without adequate WiFi security measures, cybercriminals can easily intercept the data transmitted across your network. This includes sensitive information like banking credentials, credit card numbers, personal emails, and even login information for various websites. Strong encryption protocols like WPA3 create a virtually impenetrable barrier against these types of attacks, while weak security measures (or none at all) essentially broadcast your personal information to anyone with basic hacking tools.
Boost Network Performance Through WiFi Security
Beyond the security benefits, properly securing your WiFi network can actually improve its performance. By keeping unauthorized users off your network, you ensure that your bandwidth is only used by authorized devices. This translates to faster speeds, more reliable connections, and a better overall experience when streaming, gaming, or working from home.
Don’t wait until after a security breach to take action. Check your router’s security settings today and make the necessary improvements to protect your digital life!

How to Secure Your WiFi Network
Quick Overview of WiFi Security Essentials
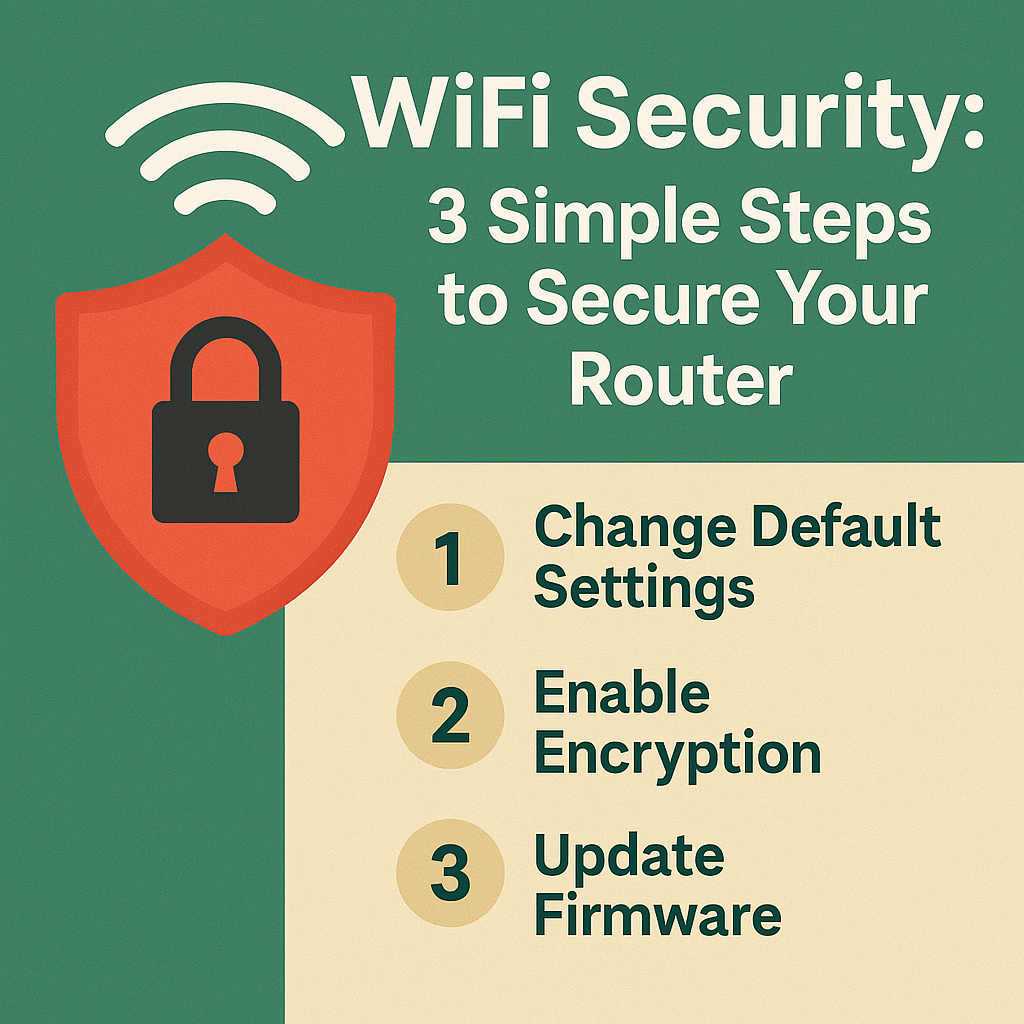
Securing your WiFi network doesn’t require a degree in computer science—it’s actually quite straightforward. With just a few simple changes to your router’s settings, you can drastically improve your WiFi security and protect yourself from most common threats. The key elements of a secure WiFi network include strong, unique passwords, modern encryption standards, and regular software updates—all of which can be implemented in less than 30 minutes.
Key Steps to Strengthen WiFi Security
1. Change Default Router Credentials
The first and most crucial step in WiFi security is changing your router’s default username and password. Manufacturers often use predictable default credentials (like “admin/admin” or “admin/password”) that hackers can easily find online. Create a strong, unique administrator password for your router that’s different from your WiFi password.
2. Implement Strong Encryption
Enable WPA3 encryption if your router supports it—it’s currently the strongest WiFi security protocol available. If WPA3 isn’t available, use WPA2-PSK (AES), which still provides solid protection. Avoid older protocols like WEP or WPA, as they have known vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit.
3. Disable Remote Management and WPS
Remote management allows you to access your router settings from outside your network—a convenience that creates unnecessary risk. Similarly, WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) makes it easier to connect devices but has security flaws. Disabling both features significantly reduces potential entry points for attackers.
4. Consider Hiding Your SSID
While not foolproof, hiding your network name (SSID) prevents it from appearing in the list of available networks on devices. This won’t stop determined hackers but adds a small layer of protection against casual intruders.
5. Set Up a Guest Network
Many modern routers allow you to create a separate guest network with its own password. This lets visitors connect to the internet without accessing your main network, where your personal devices and files are connected.
6. Update Router Firmware Regularly
Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates that patch security vulnerabilities. Check for updates every few months and apply them promptly to ensure your WiFi security stays current against evolving threats.
Step-by-Step Guide to Securing Your WiFi
Step 1: Access Your Router’s Administration Panel
- Open your web browser and enter your router’s IP address (commonly 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1)
- Log in with your username and password (if you’ve never changed these, look for default credentials on the router itself or in the manual)
Step 2: Change Default Passwords
- Navigate to the Administration or Security settings
- Change the router admin password to a strong, unique password
- Find the wireless or WiFi settings and change your network password (use at least 12 characters including uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols)
Step 3: Update Encryption Settings
- In the wireless security section, select WPA3 if available
- If WPA3 isn’t an option, choose WPA2-PSK with AES encryption
- Save your settings (your router may restart)
Step 4: Disable Unnecessary Features
- Find Remote Management settings and ensure they’re turned off
- Locate WPS settings and disable this feature
- If desired, find the option to hide SSID and enable it
Step 5: Create a Guest Network
- Look for Guest Network settings in your router’s interface
- Enable the guest network feature
- Set a separate password for the guest network
- Enable isolation to prevent guest devices from accessing your main network
Step 6: Update Router Firmware
- Navigate to the Administration or Advanced Settings section
- Look for Firmware Update or similar option
- Check for available updates and follow instructions to install them
After completing these steps, reconnect your devices using the new security settings. You’ve now significantly enhanced your WiFi security with just a few configuration changes!
Common WiFi Security Threats and How to Avoid Them
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
In this type of attack, hackers position themselves between your device and the router, intercepting data traveling between them. All information passing through—including passwords, credit card details, and private messages—can be captured and stolen.
Prevention: Use websites with HTTPS encryption (look for the padlock icon in your browser), and ensure your router uses WPA2 or WPA3 encryption. Consider using a VPN for an additional layer of WiFi security, especially when handling sensitive information.
WiFi Eavesdropping and Packet Sniffing
Similar to MITM attacks, eavesdropping involves capturing data packets traveling through your WiFi network. With specialized software tools, attackers can reassemble and read this information if it’s not properly encrypted.
Prevention: Strong WiFi security encryption (WPA2/WPA3) makes the intercepted data unreadable. Additionally, using a VPN encrypts all your internet traffic, providing protection even on networks with weaker security.
Router Malware Infections
Hackers can install malicious software on vulnerable routers, allowing them to control your internet traffic, redirect you to fake websites, or use your network for cyberattacks.
Prevention: Regularly update your router’s firmware to patch security vulnerabilities. Change default login credentials, and periodically check your router’s DNS settings for any suspicious changes.
Weak Password Vulnerabilities
The simplest and most common WiFi security vulnerability remains weak passwords. Hackers use “dictionary attacks” and “brute force” methods that can crack simple passwords in minutes.
Prevention: Use complex WiFi passwords with at least 12 characters, including a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Change your password periodically, such as every 3-6 months.
WiFi Security vs. Public Networks
Your home WiFi network and public hotspots present drastically different security landscapes. While you control your home network’s security, public WiFi at coffee shops, airports, and hotels is often minimally secured or completely open.
On public networks, other users can potentially see your online activity using basic monitoring tools. These networks are also prime targets for “evil twin” attacks, where hackers set up rogue access points with similar names to legitimate networks (like “Airport_Free_WiFi” vs. the real “Airport-Free-WiFi”).
When using public WiFi, always:
- Use a VPN to encrypt all your internet traffic
- Avoid accessing sensitive accounts (banking, email, etc.)
- Disable file sharing and AirDrop features
- Verify network names before connecting
- Use your phone’s mobile data instead when handling sensitive information
Even with these precautions, your home network with proper WiFi security measures implemented will always be significantly safer than any public WiFi connection.
Advanced Tips for Ultimate WiFi Security
Implement MAC Address Filtering
Every network device has a unique identifier called a MAC address. Most routers allow you to create a whitelist of approved MAC addresses, preventing any unlisted devices from connecting to your network. While determined hackers can spoof MAC addresses, this feature adds another barrier against casual intruders.
To set this up:
- Collect the MAC addresses of all your authorized devices
- Access your router’s settings and find the MAC filtering section
- Enable the feature and add each address to the approved list
Use a Dedicated Firewall for Enhanced WiFi Security
While most routers include basic firewall functionality, a dedicated hardware or software firewall provides significantly stronger protection. A good firewall monitors all incoming and outgoing traffic, blocking suspicious connections and protecting against various network-based attacks.
For most home users, a software firewall (like those built into Windows or macOS) provides sufficient protection when properly configured. For businesses or those with higher security needs, consider investing in a dedicated hardware firewall appliance like those offered by Fortinet, Sophos, or SonicWall.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication for Router Access
Some newer router models support two-factor authentication (2FA) for administrative access. This requires both your password and a second verification method (typically a code sent to your phone) when logging into your router settings.
If your router supports this feature, enabling it prevents unauthorized changes to your network configuration, even if someone discovers your admin password.
Monitor Connected Devices Regularly
Make it a habit to periodically check which devices are connected to your network. Most modern routers have a section showing all connected devices, usually under “Connected Devices” or “Client List.”
If you spot unfamiliar devices, change your WiFi password immediately and reconnect only your authorized devices with the new credentials. This simple practice helps ensure your WiFi security hasn’t been compromised.
Final Thoughts: Is Your WiFi Secure?
In today’s hyperconnected world, WiFi security isn’t just a technical consideration—it’s an essential part of protecting your digital life. The few minutes you spend securing your router can save you from hours of dealing with identity theft, data breaches, or compromised accounts.
Use this quick checklist to assess your current WiFi security status:
- [ ] Router admin password changed from default
- [ ] Strong, unique WiFi password in place (WPA2 or WPA3)
- [ ] Router firmware updated to latest version
- [ ] Remote management disabled
- [ ] WPS turned off
- [ ] Guest network configured for visitors
- [ ] Connected devices list checked regularly
Remember that WiFi security isn’t a one-time task—it requires periodic maintenance and updates as new vulnerabilities are discovered and patched. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you’ve taken significant steps toward creating a secure digital environment for yourself and your family.
Don’t wait for a security breach to take action. Invest a few minutes now to secure your WiFi network, and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with knowing your digital home has a strong, secure foundation.
Recommended WiFi Range Extender Resources
If you’re experiencing weak WiFi signals in certain areas of your home or office, a WiFi range extender might be the perfect solution to complement your newly secured network. Before purchasing, check out these helpful resources:
| Article Link | Description |
|---|---|
| 10 Reasons To Invest In A WiFi Range Extender Right Now | Discover the compelling benefits of adding a WiFi range extender to your network setup |
| Why You Need A WiFi Range Extender For Better Connectivity Today | Learn how a WiFi range extender can significantly improve your network’s reach and performance |
| How To Boost Your Signal With A WiFi Range Extender In 5 Easy Steps | Follow this simple guide to properly install and configure your WiFi range extender |
| WiFi Range Extender: 5 Key Differences Between New Models | Understand the important features that distinguish current WiFi extender models |
| WiFi Range Extender: How 5 Simple Settings Maximize Your Coverage | Optimize your extender’s performance with these crucial configuration adjustments |
| WiFi Range Extender: 8 Must-Know Tricks For Better Coverage | Expert tips to get the most from your WiFi extender investment |
| WiFi Range Extender: 5 Reasons Your Signal Is Weak | Troubleshoot common issues affecting your WiFi extender’s performance |
Frequently Asked Questions About WiFi Security
What is the most secure WiFi security protocol available today?
WPA3 is currently the most secure WiFi security protocol. It provides stronger encryption and better protection against common attacks compared to older standards like WPA2 or WEP. If your router supports WPA3, you should enable it immediately for maximum security.
How do security appliances like Fortigate 40F WiFi enhance network protection?
Security appliances like the Fortigate 40F WiFi combine router functionality with advanced security features such as intrusion prevention, content filtering, and application control. These unified threat management systems provide enterprise-grade WiFi protection for homes and small businesses, offering significantly stronger security than standard consumer routers.
What makes the SonicWave 224w different from regular WiFi routers?
The SonicWave 224w is a business-grade wireless access point with built-in security features. Unlike consumer routers, it integrates with SonicWall’s security ecosystem, providing real-time threat intelligence, automatic security updates, and advanced encryption. This makes it ideal for businesses requiring robust WiFi security in compliance with industry regulations.
Which WiFi security types should I avoid using?
Avoid using WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) and original WPA, as both have serious security vulnerabilities that can be easily exploited. Even WPA2 has known weaknesses, though it’s still acceptable if WPA3 isn’t available on your device. Open networks (no password) should never be used for home or business networks.
Are WiFi security apps worth installing on my devices?
WiFi security apps can provide additional protection by scanning networks for vulnerabilities, detecting potential threats, and alerting you to suspicious activities. While not a replacement for proper router security, apps like Wifi Protection or V380 Pro WiFi Security Camera apps can add an extra layer of security awareness, especially when connecting to public networks.
How do Sophos wireless access points differ from consumer WiFi routers?
Sophos wireless access points offer enterprise-level WiFi security features including granular access controls, detailed traffic analysis, and integration with comprehensive security systems. They’re designed for business environments requiring advanced threat protection and centralized management of multiple access points across locations.
What’s the difference between WiFi security and WiFi protection?
WiFi security typically refers to the encryption protocols (like WPA3) that protect data transmitted over your network. WiFi protection is a broader term encompassing additional security measures like firewalls, intrusion detection, content filtering, and malware scanning that protect devices connected to the network.
How will WiFi 7 routers improve network security compared to current models?
Upcoming WiFi 7 routers will include enhanced security features like improved encryption, better protection against physical layer attacks, and more sophisticated authentication mechanisms. They’ll also offer faster speeds and lower latency, reducing the window of opportunity for certain types of attacks.
What should I do if I suspect my WiFi security has been compromised?
If you suspect your network has been compromised, immediately change your router’s admin password and WiFi password, update the firmware, and reset to factory settings if necessary. Scan all connected devices for malware, check for unauthorized DNS changes, and consider enabling additional security features like MAC filtering or a guest network.
Is a WiFi network with Frontier security features safer than standard setups?
WiFi security with Frontier and similar provider-specific security features can offer advantages like automatic updates, remote monitoring, and preconfigured security settings. However, these conveniences shouldn’t replace understanding basic security principles. Always verify which WiFi security protocols are being used and supplement with additional measures as needed.