WiFi Range Extender: 5 Reasons Your Signal Is Weak
Are you tired of losing your WiFi connection just when you need it most? WiFi range extenders might be the solution you’ve been looking for. In today’s hyper-connected world, dead zones in your home can feel like stepping back in time. Whether you’re working remotely, streaming your favorite show, or simply browsing social media, a weak WiFi signal can quickly become a major frustration.
Did you know that the average household now has more than 20 connected devices? Yet most standard routers are only designed to cover about 1,500 square feet effectively – leaving many homes with significant coverage gaps. This disconnect between our connectivity needs and what basic equipment provides explains why so many of us experience digital “dead zones.”
Think of your WiFi signal like a conversation – the further away you move from the speaker, the harder it becomes to hear what they’re saying. Eventually, you can’t make out their words at all. WiFi range extenders act like friendly intermediaries, repeating that conversation so you can hear it clearly across greater distances.
Ready to banish those frustrating buffering symbols and “connection lost” messages for good? Let’s explore how WiFi range extenders can transform your home’s connectivity and why they might be exactly what you need for seamless, whole-home internet.
Table of Contents
What is a WiFi Range Extender?
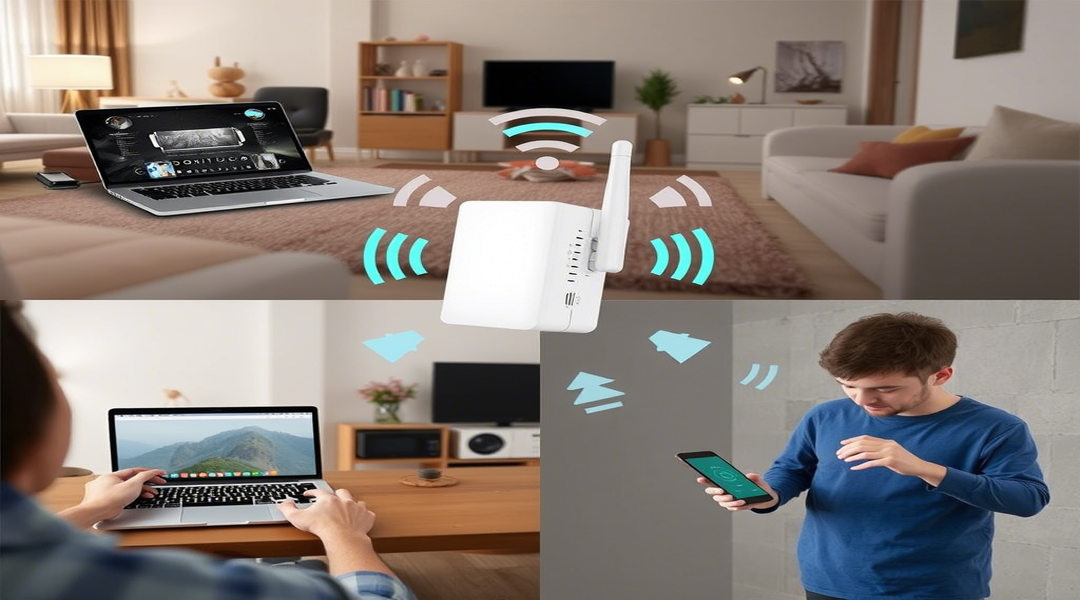
Have you ever wished your WiFi signal could reach just a little bit further? That’s exactly what a WiFi range extender does – it captures your existing WiFi signal and rebroadcasts it to create extended coverage. Think of it as a signal relay team, passing your internet connection to areas your router can’t reach on its own.
Interestingly, range extenders use the same technology as your router but in reverse – while routers convert wired internet connections into wireless signals, extenders receive wireless signals and then amplify and retransmit them. This simple yet effective approach can double your coverage area with minimal setup!
If your home has rooms where video calls freeze, websites load slowly, or streaming services buffer constantly, a WiFi range extender might be just what you need to bring reliable connectivity to every corner.
Why You Should Consider a WiFi Range Extender
Eliminate Dead Zones with a WiFi Range Extender
Nothing’s more frustrating than walking to another room only to see your video call freeze or download stop. WiFi range extenders excel at filling those connectivity gaps, bringing reliable signals to previously dead areas of your home. Whether it’s reaching upstairs bedrooms, basement offices, or backyard patios, an extender ensures your connection follows you wherever you go.
Most standard routers broadcast in a radial pattern that weakens with distance and struggles with physical barriers like walls and floors. Range extenders strategically placed between your router and dead zones can bridge these gaps, creating a seamless connectivity experience throughout your entire home.
Boost Connection Speeds in Weak Signal Areas
Even in areas where your WiFi technically reaches, a weak signal often means painfully slow speeds. WiFi range extenders not only extend coverage but can significantly improve connection quality in these fringe areas. The difference can be dramatic – turning frustrating 1-2 Mbps connections that barely load basic websites into robust 20+ Mbps connections that handle HD streaming with ease.
By strengthening signal quality in previously weak areas, extenders ensure your devices maintain faster, more reliable connections that support bandwidth-intensive activities like video conferencing, gaming, and 4K streaming.
Support Multiple Devices Without Performance Loss
Today’s homes are filled with connected devices – from smartphones and laptops to smart TVs, security cameras, and voice assistants. When all these devices compete for bandwidth from a single router, performance often suffers for everyone. A well-placed WiFi range extender helps distribute this load, ensuring every device maintains proper connectivity without slowing down the network.
This becomes especially important for homes with multiple users simultaneously streaming, gaming, or working remotely. The added coverage and capacity provided by range extenders means everyone enjoys consistent performance regardless of how many devices are connected.
Take a moment to assess your current WiFi situation. Do you have rooms where connections drop? Areas where speeds slow to a crawl? If so, a WiFi range extender could be the affordable solution you need.

How to Choose the Right WiFi Range Extender
Quick Overview
Selecting the proper WiFi range extender can mean the difference between transforming your connectivity experience and wasting money on a device that doesn’t solve your problems. The right extender should complement your existing router, match your internet plan’s capabilities, and address your specific coverage challenges.
Key features to watch for include compatibility with your router’s WiFi generation, dual-band capability to reduce interference, and appropriate speed ratings that won’t bottleneck your connection. Let’s break down these essential factors to help you make an informed decision.
Key Factors to Consider When Buying a WiFi Range Extender
Router Compatibility
Your WiFi range extender must be compatible with your existing router to work effectively. Check your router’s WiFi generation (802.11n, ac, or ax/WiFi 6) and choose an extender that supports the same or newer standards. While most extenders are backward compatible, matching technologies ensures optimal performance.
WiFi Standards
WiFi technology has evolved substantially over the years:
- 802.11n (WiFi 4): Older standard with speeds up to 300 Mbps
- 802.11ac (WiFi 5): Mid-range standard supporting speeds up to 1.3 Gbps
- 802.11ax (WiFi 6): Newest standard with speeds up to 9.6 Gbps and better handling of multiple devices
For most homes today, a WiFi 5 (802.11ac) or WiFi 6 (802.11ax) extender provides the best balance of performance and value.
Frequency Bands
WiFi range extenders typically offer single-band (2.4GHz only) or dual-band (2.4GHz and 5GHz) operation:
- 2.4GHz: Longer range but slower speeds and more prone to interference
- 5GHz: Faster speeds but shorter range and better at avoiding interference
Dual-band extenders are generally worth the extra cost as they provide flexibility and can significantly reduce interference issues that plague many home networks.
Speed and Performance Ratings
Manufacturers advertise theoretical maximum speeds that you’ll rarely achieve in real-world conditions. However, these ratings still provide a useful comparison point:
- AC750: Entry-level dual-band performance (300+450 Mbps)
- AC1200: Mid-range performance (300+867 Mbps)
- AC1750 and above: High-performance options for larger homes or faster internet plans
Match your extender’s capabilities to your internet service plan. If you pay for 100 Mbps internet, an AC1200 extender would be sufficient, while gigabit internet users should consider higher-performance models.
Size and Design
WiFi range extenders come in various form factors:
- Plug-in models that connect directly to wall outlets
- Desktop versions that sit on surfaces
- Weatherproof outdoor models for extending coverage to yards or outbuildings
Consider where you’ll place your extender and choose a design that fits that location without causing obstruction or becoming an eyesore.

Setup Complexity
Some extenders feature WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) buttons that make connection as simple as pressing a button on both your router and extender. Others require more involved configuration through web interfaces or mobile apps. Consider your comfort level with technology when choosing between simpler or more feature-rich options.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Your WiFi Range Extender
Setting up your new WiFi range extender doesn’t have to be complicated. Follow these straightforward steps to get your extended network up and running quickly:
- Find the optimal location: Place your extender about halfway between your router and the dead zone you want to cover. Ensure it’s within range of your existing WiFi signal but close enough to extend coverage to needed areas.
- Connect to power: Plug your extender into an electrical outlet and wait for it to power on completely (usually indicated by status lights).
- Access the setup interface: Most extenders offer two setup methods:
- WPS Method: Press the WPS button on your router, then press the WPS button on your extender within 2 minutes.
- Manual Method: Connect to the extender’s default WiFi network (usually listed on the device or in instructions), then open a web browser and enter the configuration address (typically 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1).
- Configure network settings: Follow the on-screen instructions to:
- Select your existing WiFi network
- Enter your WiFi password
- Choose names for your extended networks (some extenders automatically add “_EXT” to your existing network name)
- Set a password for the extended network (using the same password as your main network simplifies connections)
- Finalize setup: After configuration, your extender will reboot and establish connection to your main router.
- Verify coverage: Use a smartphone or laptop to test connectivity in previously dead zones. If coverage is still spotty, try repositioning your extender slightly.
- Connect your devices: Connect your devices to the extended network, particularly in areas that previously had weak coverage.
Remember, the ideal location for your extender is crucial for optimal performance. If you’re still experiencing connectivity issues after setup, try different positions until you find the sweet spot.
Common WiFi Extension Problems and How to Solve Them
Even with a properly installed WiFi range extender, you might encounter some challenges. Here are common issues and their solutions:
Signal Interference
Problem: Reduced speeds or intermittent connectivity due to interference from other devices.
Solution: Keep your extender away from potential interference sources like microwaves, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, and baby monitors. Using the 5GHz band can also help reduce interference from common household devices, most of which operate on 2.4GHz.
Suboptimal Placement
Problem: Weak signal despite having an extender installed.
Solution: The golden rule for extender placement is finding the midpoint where your router’s signal is still strong. Too close to the router wastes potential coverage; too far and the extender receives a weak signal to rebroadcast. Try several locations and test signal strength using WiFi analyzer apps to find the optimal position.
Connection Dropping
Problem: Devices disconnect from the extended network unexpectedly.
Solution: Check if your extender is overheating (which can cause automatic shutdowns) or if too many devices are connected simultaneously. Some extenders also benefit from periodic reboots – consider setting up an outlet timer to automatically restart it weekly during low-usage hours.
Slow Speeds After Extension
Problem: Noticeably slower connection on the extended network compared to main router.
Solution: This is normal to some extent – extenders typically reduce bandwidth by approximately half since they must receive and rebroadcast signals. To minimize this effect:
- Use dual-band extenders that can receive on one band and transmit on another
- Consider upgrading to a tri-band extender for high-demand environments
- Try using Ethernet backhaul if your extender supports it, connecting it to your router via cable for more reliable backhaul traffic
Different Network Names Causing Confusion
Problem: Devices don’t seamlessly transition between main and extended networks.
Solution: Some extenders allow you to use the same SSID (network name) as your main network, which can help devices transition more seamlessly. However, this may cause connection issues in some cases. If you use different names, you’ll need to manually connect to the stronger network when moving between coverage areas.

WiFi Range Extenders vs. Mesh WiFi Systems
As you consider solutions for your WiFi coverage issues, it’s worth understanding the differences between traditional range extenders and newer mesh WiFi systems.
Traditional WiFi Range Extenders
Pros:
- More affordable entry point (starting around $20-30)
- Simple to add to existing network without replacing your router
- Good solution for smaller homes with just 1-2 dead zones
Cons:
- Can create separate network names requiring manual switching
- Often halve the bandwidth due to signal rebroadcasting
- May introduce latency (delay) in connections
- Generally more limited management options
Mesh WiFi Systems
Pros:
- Create a single, seamless network throughout your home
- Automatically manage device connections to optimal nodes
- Usually offer more consistent speeds throughout coverage area
- Feature sophisticated management apps with parental controls and security features
- More aesthetically pleasing designs meant to be visible in your home
Cons:
- Significantly more expensive (starting around $150-300 for multi-unit systems)
- Requires replacing your existing router rather than supplementing it
- May be overkill for smaller homes or simple needs
Which is Right for Your Home?
Consider a traditional WiFi range extender if:
- You have a smaller home (under 2,000 sq ft)
- You only have 1-2 problem areas needing coverage
- You’re on a tighter budget
- You want to keep your existing router
Consider a mesh WiFi system if:
- You have a larger home (over 2,000 sq ft)
- You have multiple dead zones throughout your home
- You value seamless roaming without network switching
- You’re willing to invest more for a comprehensive solution
- You’re comfortable replacing your current router completely
For many homes, the best approach might be starting with a quality range extender like the WiFi Extender Signal Booster featured in this article, and upgrading to a mesh system later if needs evolve.
Advanced Tips for Optimizing Your Extended WiFi Network
Once you’ve set up your WiFi range extender, these expert-level tips can help you achieve peak performance:
Strategic Placement for Maximum Coverage
Beyond the basic halfway rule, consider these placement refinements:
- Position extenders higher up (on shelves or mounted) for better signal propagation
- Avoid corners; central locations within rooms provide better omnidirectional coverage
- Keep at least 10 feet away from large metal objects, which can block signals
- In multi-story homes, place extenders directly above or below your router for better vertical coverage
Use WiFi Analyzer Apps to Find Dead Zones
Free apps like “WiFi Analyzer” (Android) or “NetSpot” (Mac/Windows) can:
- Create visual heat maps of your coverage
- Identify specific dead zones before placing extenders
- Help determine interference from neighboring networks
- Confirm improvements after installation
Take signal readings in various locations around your home to identify the perfect extender placement.
Network Name Strategies for Optimal Performance
You have two primary options for network naming:
- Same SSID approach: Configure your extender to use identical network names/passwords as your main router. This creates a more seamless experience but may occasionally cause devices to “stick” to weaker connections.
- Different SSID approach: Use distinct names (like “HomeWiFi” and “HomeWiFi_Ext”). This gives you manual control over which network your devices connect to, ensuring you always get the strongest signal when you need it.
For most users, the same SSID approach offers the best balance of convenience and performance.
Managing Device Connections
Not all devices need the same connection quality:
- Connect stationary, high-bandwidth devices (smart TVs, gaming consoles) directly to the closest access point
- Reserve 5GHz connections for devices that need speed over range
- Use 2.4GHz for devices that need reliability over distance (like security cameras)
- Consider enabling QoS (Quality of Service) settings to prioritize important devices or applications
WiFi Extender Spotlight: WiFi Extender Signal Booster for Home
For those seeking a reliable solution to WiFi dead zones, the WiFi Extender Signal Booster for Home offers impressive features at an affordable price point.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Up to 6500 Sq.Ft |
| Device Support | 45+ devices simultaneously |
| Power Mode | Standard Power Supply |
| Operating Voltage | 110V/220V compatible |
| Plug Type | US Plug |
| Color Options | Black |
| Rating | 4.6/5 stars (24K+ sold) |
| Regular Price | $49.99 |
| Current Price | $12.87 (74% OFF) |
This highly-rated extender ranks #12 in WiFi & Networking products, making it a trusted choice for thousands of users. Its expansive coverage area makes it suitable for even larger homes, while the ability to support 45+ devices ensures your entire household’s connected devices maintain strong connections.
Check current pricing and availability
Final Thoughts: Is Your WiFi Coverage Complete?
In today’s connected world, comprehensive WiFi coverage isn’t a luxury—it’s a necessity. From remote work and virtual learning to streaming entertainment and smart home functionality, reliable internet throughout your home forms the foundation of our digital lives.
A quality WiFi range extender like the one featured above can transform your connectivity experience, eliminating frustrating dead zones and ensuring every corner of your home enjoys robust, reliable internet access.
Ask yourself:
- Can I connect from every room without signal drops?
- Do my video calls maintain quality regardless of where I take them?
- Can multiple family members stream, game, or work simultaneously without issues?
- Does my smart home technology function reliably throughout my home?
If you answered “no” to any of these questions, it’s time to consider a WiFi range extender. With today’s affordable options offering extensive coverage and simple setup, there’s no reason to tolerate connectivity gaps in your home any longer.
Take action today to extend your network’s reach and enjoy seamless connectivity throughout your entire home. Your future self—free from buffering symbols and “reconnecting” messages—will thank you!

Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a WiFi extender and a WiFi booster?
The terms “WiFi extender” and “WiFi booster” are often used interchangeably in the marketplace. Technically speaking, a WiFi extender captures your existing signal and rebroadcasts it to extend coverage, while some products marketed as “boosters” might focus more on amplifying the existing signal. However, in practice, most devices sold under either name perform virtually identical functions.
How does a TP-Link WiFi extender compare to other brands?
TP-Link is one of the most established names in networking equipment, offering reliable performance at competitive prices. Their extenders, particularly the popular RE220 and RE315 models, are known for user-friendly setup and consistent performance. That said, brands like Netgear and Linksys also offer excellent options with various feature sets and price points to consider.
What’s the easiest WiFi extender setup process?
Most modern WiFi extenders feature WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) functionality, allowing connection with a simple button press on both your router and the extender. For models without WPS, web-based setup interfaces have become increasingly user-friendly, often guided by mobile apps that walk you through the process step by step.
Are mesh WiFi extenders better than traditional extenders?
Mesh WiFi systems create a more seamless experience than traditional extenders, with behind-the-scenes technology that automatically manages connections and ensures devices connect to the strongest access point. However, they’re typically more expensive and require replacing your existing router. For many households, traditional extenders provide an excellent balance of performance and value.
Will a WiFi extender help with my Xfinity/Cox internet service?
Yes, WiFi extenders work with any internet service provider, including Xfinity and Cox. They extend the wireless network created by your router, regardless of which company provides your internet service. Some providers like Xfinity offer their own extenders (like xFi Pods), which may integrate more deeply with their gateway devices but generally perform the same function as third-party options.
What’s the best WiFi extender for gaming?
Gamers should prioritize extenders with low latency and strong 5GHz performance. Look for models advertising gaming features like dedicated QoS (Quality of Service) settings that prioritize gaming traffic. Dual or tri-band extenders with backhaul capabilities (either wireless or Ethernet) maintain more bandwidth for consistent gaming performance.
Can a WiFi extender help with my Ring doorbell connection?
Absolutely! Ring doorbells and other smart home devices often suffer from weak connections due to their placement at the periphery of your home. A strategically placed WiFi extender can significantly improve reliability for these devices. Some extenders are even specifically marketed for outdoor coverage to help with devices like security cameras and doorbells.
How does a wireless internet booster improve my connection speed?
While extenders won’t increase your baseline internet speed (determined by your service plan), they can dramatically improve real-world performance in previously weak coverage areas. A device receiving a stronger signal can utilize more of your available bandwidth, turning an unstable 1-2 Mbps connection into a reliable 20+ Mbps connection in formerly dead zones.